Multinational Enterprises Since Covid: Stronger Than Domestic Firms, Especially at Home
Constance Marette
Camilo Umana Dajud
Vincent Vicard
Constance Marette
Camilo Umana Dajud
Vincent Vicard
The Covid-19 crisis heightened awareness of the vulnerabilities inherent in global trade, prompting a re-evaluation of the benefits and risks of globalization. Although global trade openness briefly declined – reflecting a sharper drop in trade than in GDP during lockdowns – it quickly rebounded to pre-crisis levels. However, this aggregate trend may conceal significant microeconomic shifts in firm behavior. In particular, the employment responses of multinational enterprises (MNEs), which play a central role in global value chains, offer valuable insights into the reshaping of the global trading system. Post-crisis, MNEs exhibited stronger employment resilience than purely domestic firms, especially within their home-country affiliates. This home bias in MNE responses may signal the early stages of a reshoring trend.
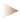 Data : let451_EN.xlsx
Data : let451_EN.xlsx
|
|
Subscribe to La Lettre du CEPII with our RSS feed https://www.cepii.fr/CEPII/rss/RSSLettre.asp |
Back





